API Handlers
This feature is available since version 24.7. releases.
Introduction
API handlers offer ability to attach custom flows to API in cross-cutting way by specifying request url regex pattern.
It's possible to add flows at the start or end of API execution, as well as on error.
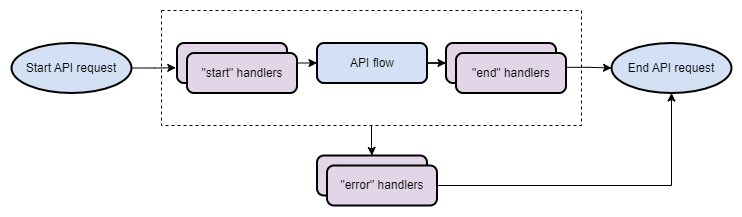
Handler execution
Handler flow is executed if handler path pattern (regex) matches incoming request path or if it is directly attached to API.
Request path can differ from API path defined in Dynamic API definition:
- Request path doesn't include query parameters
- Request path may include base path defined in routes
- Request path includes path parameter values, while API path includes path parameter placeholders
As there can be multiple matching handlers for the API call, order of execution is determined by order property
defined when creating handler.
Depending on event type it is executed at the start of API execution, at the end of API execution or in case
of error.
Change API flow
When changing API flow using external parameters it is important to validate the input to prevent security issues.
Specific for start handler is ability to change the main flow which is executed by API endpoint. This is done by
setting reserved doc aceApiFlow property during start handler execution.
For example if API has attached flow getPolicies, but start handler has set aceApiFlow to getPoliciesV2, then
getPoliciesV2 flow will be executed.
It can be used together with API context to dynamically change the flow based on API properties.
For example following step would change flow based on version parameter and if version would be v2,
then v2/getPolicies flow would be executed.
- name: Step jsonata
config:
maps:
- targetPath: aceApiFlow
jsonata: version & '/' & $api.flow
stepType: jsonata
API context
API custom properties are available only when using split API files
As one handler can be executed for multiple API calls in cross-cutting way, it might be useful to implement different
logic based on API context. API context is available in $api variable, and it
contains details about Dynamic API, as
well as API custom properties which can be used to turn on/off specific logic in handler. For example if API has custom
property public: true, then it's possible to access this property in flow by $api.customProperties.public.
Error handlers
If handler or API flow (the one attached to api endpoint) has unhandled error, then ACE processes it in following way:
- Further API execution is stopped - other flows (handler or API) are not executed
- Errors ar set in
docundererrorsproperty - All error handlers which apply to API (attached by path or directly) are executed, unless
aceApiStopExecutionis set totrueindoc - If error handlers themselves contain error, then error handler execution is stopped and ACE returns error (legacy error handlers still are executed)
See API error handler example here.
Stop further API execution
All handlers and main API flow are executed in sequence unless one of few things happen:
- handler or main flow contains errors
- flow
docat the end of execution has reserved propertyaceApiStopExecutionset totrue aceApiStopExecutionproperty is set using Response step option "Stop API execution"
It becomes important if it's necessary to return custom response from start handler, as setting result property
alone won't stop further execution. It's also necessary to set aceApiStopExecution to true to stop other flows from
executing.
Creating handler
To create handler:
- Click on Handlers on the left side menu.
- Then click on + NEW HANDLER button.
- Define handler's properties
- Press save button
Properties
Name- a handler namePath pattern- regex to match the path of the API endpoint. You can use.regex to match all paths.Event- when handler gets executed (start/end/error).starthandler gets executed before API flow,endhandler get executed after API flow. In case oferrorhandler, it will be executed only if error is thrown by other handlers or by API flow(the one attached to api endpoint).Flow- flow to be run when this handler gets executed.Order- order of handler execution, by default0. Let's say, there is a case when twostarthandlers meet the criteria to be executed for api call. In such cases those two handlers will be sorted by order(numerically) or as a fallback by their name alphabetically.