Security
The goal of this article is to explain ACE capabilities and various scenarios how API consumers can be Authenticated and Authorized in the Production environment.
Management APIs
The purpose of ACE Management APIs is to expose and allow a manipulation of the ACE configuration.
There are several options how to protect these APIs.
SSH
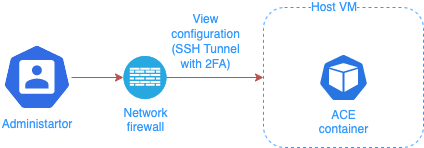
Administrator user uses the same credentials and transport as to connect to Host to manage the operating system, to establish SSH tunnels necessary to manage the ACE configuration.
Use the Network firewall to make sure that ACE management APIs port can be accessed only locally using SSH tunnel.
OpenID Connect as Sidecar (Express Gateway)
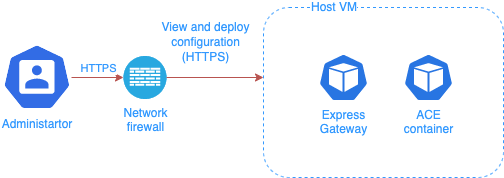
Express Gateway is deployed as a sidecar to act as a API Gateway and Identity Provider.
Administrator user connects to Express Gateway sidecar to manage the ACE configuration.
Use the Network firewall to make sure that ACE management APIs port can be accessed only locally through Express Gateway Sidecar.
OpenID Connect external Identity Provider (Keycloak)
ACE container is deployed as HTTP service and requires a Sidecar or Ingress to handle HTTPS.
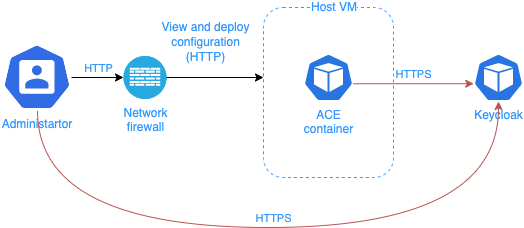
ACE can be configured to use external OpenID Connect compatible Identity Provider to authenticate the Administrator users.
When Administrator user connects to ACE container, he is redirected to external Identity Provider to authenticate himself.
Use the Network firewall to make sure that ACE management APIs port can be accessed only from the trusted network.
Dynamic APIs
Dynamic APIs are APIs that are built by Domain Experts.
Dynamic APis can be either Anonymous or Authenticated, depending on the business logic built into these APIs.
Anonymous APIs are used by consumers who have not yet been identified in the system and are usually in inception phase of the business process (for example a new Customer who seeks to get a quotation for a financial product).
Authenticated APIs are used by consumers that are already know to the system and are coming to access assets that they have previously have stored in the system (for example an existing Customer reviewing his quotes and policies).
API gateway
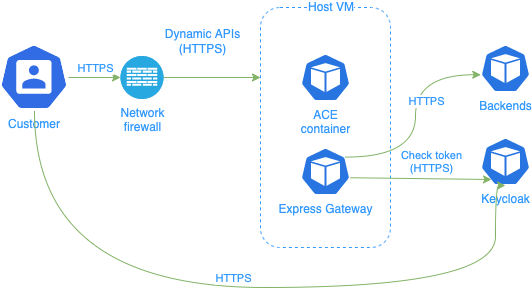
Express Gateway is deployed as a sidecar to act as the API Gateway.
Customer connects to Express Gateway sidecar to access Dynamic APIs.
Customer is redirected by Mobile or Web application to Identity Provider (Keycloak) to identify himself, if he is attempting to access application functional areas that require authentication.
Use the Network firewall to make sure that ACE Dynamic APIs port can be accessed only locally through Express Gateway Sidecar.
API gateway acts as an additional layer of security, to:
- make sure that only certified APIs are accessible via proper Authentication method,
- track expiration and validity of authentication tokens of
existing Customers, - ensure quality of the service by enforcing service limits (for example, API calls per minute), to make sure that Customers do not overwhelm the
Backend system, - enable
Data Loss Protectionby certifying outgoing connections that ACE container can make.
System to System Authentication
Once Customer is authenticated in API gateway, there is no practical reason to authenticate him in ACE or in Backend systems.
It is however necessary to authenticate connectivity between the systems. There are several methods how to authenticate with the peer system:
- API key,
- Username and Password (Basic Authorization),
- Mutual SSL
Authorization
ACE can act as an additional authorization layer:
- in case if Backend does not support anonymous users, ACE can limit the scope of Backend functionality that
new Customerscan access, - in case if Backend lacks granularity of
data row level security, but rather has system to system APIs thatrestrict user to certain functional zones(for example, Backend can allow access to only Policy objects for a particular Agent, but lacks capabilities to limit user access to a particular Policy object).
CORS
It's necessary to configure CORS headers to allow requests only from trusted domains. CORS configuration is typically done in Ingress or API gateway.
Secrets
Any secrets (for example passwords) must be passed as the environment variables to the Flow Runner container.
Environment variables are accessible in flow as $env object properties.
Environment variables with secrets should not be stored unencrypted on the persistent storage.
Instead they must be loaded from vault and passed to the Flow Runner container as (for example in Kubernetes) as environment variables.